Efficiency and equality and the role of government dse
在現代社會,效率和公平成為了許多政策制定者和公民關注的焦點。效率代表著如何在最少的時間和成本內達到最大的生產力和效益;而公平則是指每個人都能夠平等地享受社會資源和福利。然而,實現效率和公平之間往往存在矛盾,因為追求效率可能會導致資源分配不公平,而強調公平可能會降低效率。
政府在這個方程式中扮演著至關重要的角色。政府的政策和行動可以促進效率和公平的達成,但同時也需要考慮到這兩者之間的平衡。政府可以通過設定規則、提供資源、培育創新等方式來推動效率和公平的實現。此外,政府還可以通過紓解貧困、提供公共服務、建立社會保障制度等方式來實現公平,從而減少社會不平等和貧富差距。
在這篇文章中,我們將探討效率、公平和政府的角色之間的關係。我們將討論政府在推動效率和公平方面所採取的策略,以及這些策略的優缺點。我們還將探討政府在實現效率和公平之間的平衡方面所面臨的挑戰,以及可能的解決方案。最後,我們將總結討論,探討政府在效率和公平之間達成平衡的重要性,以及未來政府應該如何在這個方面發揮作用。
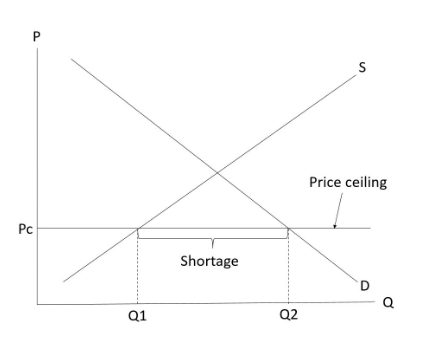
Price ceiling
-A maximum price allowed by the government/by law.
-普通商家自己將個價錢set係equilibrium下面唔算price ceiling,但同樣會出現shortage,其影響同price ceiling一樣。
-Effective only when it is imposed below the equilibrium price.
-When the price ceiling is set above the equilibrium (i.e., ineffective), price and quantity transacted will remain at the equilibrium level.
-Example: Rent control
|
Price |
Pc |
|
Quantity transacted |
Q1 |
|
Total expenditure/revenue |
Pc x Q1 |
Point to note
Total expenditure/revenue must drop under an effective price ceiling as both price and quantity transacted decrease.
Summary on the effects of an effective price ceiling
-Price↓
-Quantity transacted↓
-Total expenditure/revenue↓
-Emergence of shortage (excess demand)
Ways to deal with a shortage resulted from the imposition of a price ceiling
-Non-price competition
-Examples: Drawing lots/First come-first serve
-Price competition
-Examples: Imposing extra fees such as entrance fees (sellers to buyers)
-Black market
-係黑市賣嘅嘢會比外面貴,價高者得。
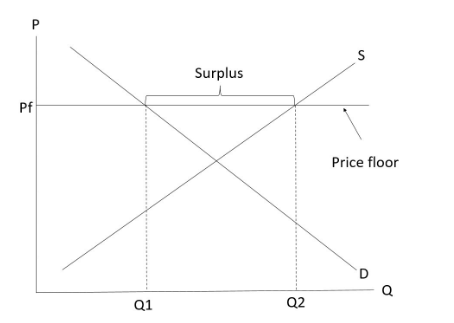
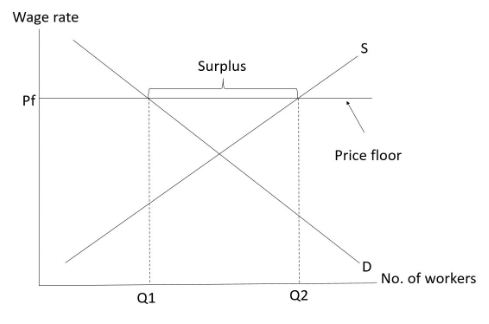
Price floor
-A minimum price allowed by the government/by law.
–普通商家自己將個價錢set係equilibrium上面唔算price floor,但同樣會出現surplus,其影響同price floor一樣。
-Effective only when it is imposed above the equilibrium price.
-When the price floor is set below the equilibrium (i.e., ineffective), price and quantity transacted will remain at the equilibrium level.
-Example: Minimum wage 最低工資 **************
|
Price |
Pf |
|
Quantity transacted |
Q1 |
|
Total expenditure/revenue |
Pf x Q1 |
Point to note
The effect on total expenditure/revenue due to a fall in price (caused by an effective price floor) should be uncertain, depending on the elasticity of demand.
Labour market under minimum wage (an effective price floor)
Point to note
-係最低工資之下,有surplus嘅係workers,即係太多workers請唔曬,唔係有shortage
Summary on the effects of an effective price ceiling
-Price↑
-Quantity transacted↓
-Total expenditure/revenue ?
-Emergence of surplus (excess supply)
Ways to deal with a surplus resulted from the imposition of a price floor
-Non-price competition
–Non-price competition
-Examples: Providing free gifts (buyers to sellers)
–Price competition
-Examples: Imposing extra fees
-Illegal price cutting by sellers
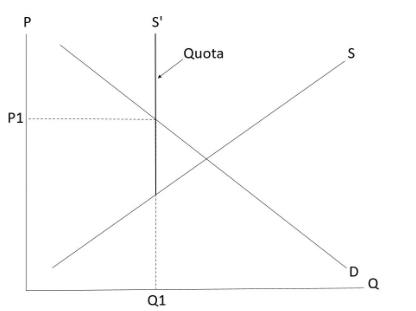
Quota
-A maximum quantity supplied of a good allowed by the government/by law.
-Effective only when it is imposed below the equilibrium quantity. (i.e.畫係equilibrium point嘅左邊)
-When the quota is set above the equilibrium quantity (畫左係equilibrium嘅右邊→ineffective), price and quantity transacted will remain at the equilibrium level.
-Example: Import/export quota
|
Price |
P1 |
|
Quantity transacted |
Q1 |
|
Total expenditure/revenue |
P1 x Q1 |
Point to note
-The effect on total expenditure/revenue due to a rise in price (caused by an effective quota) should be uncertain, depending on the elasticity of demand.
Effect on quality under quota
-As a quota would restrict the quantity of a good allowed to be sold, some producers will thus decide to improve their product quality to increase their competitiveness. Therefore, the average quality of the good under quota will increase.
-If an effective quota on a good is removed, the average quality of the good will thus deteriorate.
Summary on the effects of an effective quota
-Price↑
-Quantity transacted↓
-Total expenditure/revenue ?
-Improvement in average quality of goods
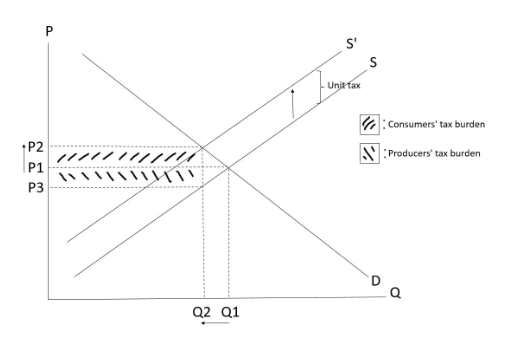
Unit tax
-Levied on every unit of output.
-Not the same as Ad valorem tax (percentage tax) which is a certain percentage of the price of a good.
Effects of a unit tax
-After the imposition of a unit tax on producers, the cost of production of producers will increase which will lead to a decrease in supply.
Point to note
-When drawing the arrow indicating the drop in supply, it should be drawn as an arrow pointing upward.
|
Original price |
P1 |
|
Price after tax = Price actually paid by consumers = Market price |
P2 |
|
Per unit revenue after tax = Price actually received by producers |
P3 |
|
Quantity transacted |
Q2 |
|
Consumers’ total expenditure |
P2 x Q2 |
|
Producers’ total revenue net of tax |
P3 x Q2 |
Consumers’ total expenditure
=Total revenue (received by producers) inclusive of tax
=Total revenue (received by producers) net of tax + total tax payment
-The change in consumers’ total expenditure should be uncertain after the imposition of a unit tax, depending on the elasticity of demand.
Producers’ total revenue net of tax
=Consumers’ total expenditure – total tax payment
=Price actually received by producers x new quantity transacted
= (New equilibrium price (P2) – Unit tax) x new quantity transacted
-Producers’ total revenue net of tax must decrease under any elasticity of demand after a unit tax is imposed as both quantity transacted, and price actually received by producers drop.
Distribution of tax burden
Total tax burden/total tax payment/total tax revenue received by government
=Consumers’ tax burden + producers’ tax burden
=Unit tax x new quantity transacted
= (P2 – P3) x Q2
Consumers’ tax burden
=Unit tax borne by consumers x new quantity transacted
= (P2 – P1) x Q2
-對於consumers黎講,比多D錢就係佢地嘅burden。
Producers’ tax burden
=Unit tax borne by producers x new quantity transacted
= (P1 – P3) x Q2
-對於producers黎講,收小D錢就係佢地嘅burden。
Summary
|
Consumers食多D |
Ed<Es |
|
Producers食多D |
Es<Ed |
|
一樣食咁多 |
Ed = Es |
越inelastic食越多,越elastic食越小
Extreme cases
|
Consumers食曬 |
Producers食曬 |
|
Perfectly inelastic demand |
Perfectly elastic demand |
|
Perfectly elastic supply |
Perfectly inelastic supply |
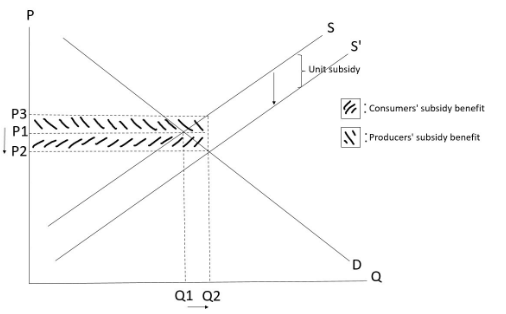
Unit subsidy
-Granted for each unit of output.
-Not the same as Ad valorem subsidy (percentage subsidy) which is a certain percentage of the price of a good.
Effects of a unit subsidy
-After the imposition of a unit subsidy on producers, the cost of production of producers will decrease which will lead to an increase in supply.
Point to note
-When drawing the arrow indicating the increase in supply, it should be drawn as an arrow pointing downward.
|
Original price |
P1 |
|
Price after subsidy = Price actually paid by consumers = Market price |
P2 |
|
Per unit revenue after subsidy = Price actually received by producers |
P3 |
|
Quantity transacted |
Q2 |
|
Consumers’ total expenditure |
P2 x Q2 |
|
Producers’ total revenue including subsidy |
P3 x Q2 |
Consumers’ total expenditure
=Producers’ total revenue excluding subsidy
-The change in consumers’ total expenditure should be uncertain after the imposition of a unit subsidy, depending on the elasticity of demand.
Producers’ total revenue including subsidy
=Consumers’ total expenditure + total amount of subsidy granted
=Price actually received by producers x new quantity transacted
= (New equilibrium price (P2) + Unit subsidy) x new quantity transacted
-Producers’ total revenue including subsidy must increase under any elasticity of demand after a unit subsidy is imposed as both quantity transacted, and price actually received by producers increase.
Distribution of subsidy
Total amount of subsidy granted (by government)
=Consumers’ subsidy benefit + producers’ subsidy benefit
=Unit subsidy x new quantity transacted
= (P3 – P2) x Q2
Consumers’ subsidy benefit
=Unit subsidy enjoyed by consumers x new quantity transacted
= (P1 – P2) x Q2
-對於consumers黎講,比小D錢就係佢地嘅benefit。
Producers’ tax burden
=Unit subsidy enjoyed by producers x new quantity transacted
= (P3 – P1) x Q2
-對於producers黎講,收多D錢就係佢地嘅benefit。
Summary
|
Consumers享受多D |
Ed<Es |
|
Producers享受多D |
Es<Ed |
|
一樣享受咁多 |
Ed = Es |
越inelastic享受越多,越elastic享受越小
Extreme cases
|
Consumers享受曬 |
Producers享受曬 |
|
Perfectly inelastic demand |
Perfectly elastic demand |
|
Perfectly elastic supply |
Perfectly inelastic supply |
如果大家有什麼補習問題,如私人補習、網上補習好唔好,歡迎你可以隨時再跟我多交流一下,可以Follow 「學博教育中心 Learn Smart Education」 Facebook page同IG得到更多補習課程資訊,亦都可以上我們的補習網頁了解更多!
DSE Econ 文章系列
Microeconomics
Macroeconomics
- 經濟表現的量度 Measure of economic performance
- 國民收入決定及價格水平 National income determination and price level
- 貨幣與銀行 Money and Banking
- 宏觀經濟問題和政策 Macroeconomic Problems and policies
- 國際貿易和金融 International Trade and Finance